Common geological hazards during tunneling construction include water inrush, landslides, rockbursts, deformation of weak surrounding rock, impacts of faults and joints, leakage of hazardous gases, and ground subsidence. These hazards and their preventive measures are described below:
1. Water inrush: When encountering aquifers during tunnel construction, large amounts of water may occur. Preventive measures include conducting geological surveys in advance to understand the distribution of groundwater; implementing appropriate drainage measures, such as installing drainage holes and pumps; and using waterproofing materials and sealing techniques during construction.
2. Landslides: Unstable rock mass at the top or side of the tunnel may suddenly collapse. Preventive measures include strengthening initial support, such as using anchors and shotcrete; timely monitoring of surrounding rock deformation and taking immediate action if any anomalies are detected; and rationally designing tunnel cross-sections and construction methods.
3. Rockburst: Under high stress conditions, the sudden rupture of rock mass releases energy, potentially causing serious damage. Preventive measures include conducting stress measurements and rock stability analysis; implementing stress relief measures such as pre-splitting blasting and hydraulic fracturing; and strengthening support and monitoring.
4. Deformation of Weak Surrounding Rock: In weak or plastic strata, the surrounding rock may experience significant deformation. Preventive measures include the use of flexible support systems, such as retractable steel arches and anchor cables; implementing phased excavation and support; and strengthening monitoring and providing timely feedback.
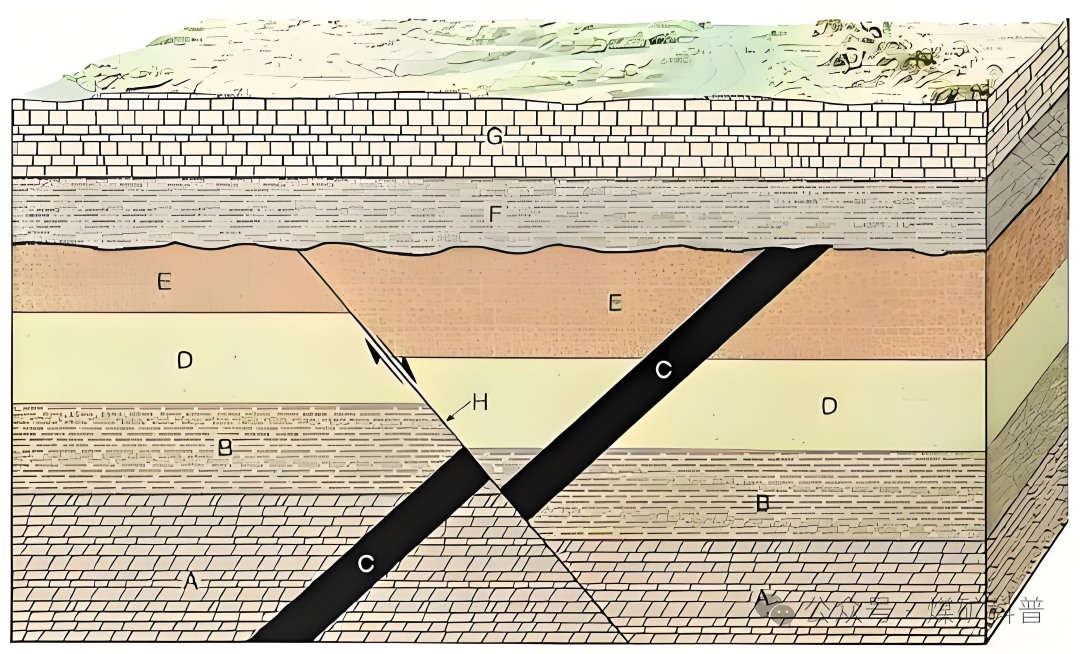
5. Fault and Joint Zones: When a tunnel passes through a fault zone, the stability of the rock mass is reduced. Preventive measures include detailed exploration of the location and characteristics of the faults; considering the impact of faults during design and implementing enhanced support measures; and exercising caution during construction to avoid activating dynamic faults.
6. Hazardous Gas Leakage: Construction in strata containing flammable gases may result in hazardous gas leaks. Preventive measures include conducting gas monitoring to ensure construction safety; using ventilation systems to remove hazardous gases; and equipping with personal protective equipment.
7. Ground Subsidence: Tunnel construction may cause ground subsidence, which may affect surface structures. Preventive measures include the use of construction methods such as shield tunneling to minimize ground impacts; strengthening ground monitoring and implementing timely remedial measures; and considering the impact of ground subsidence during the design phase.
In order to effectively prevent these geological disasters, sufficient geological exploration and risk assessment should be carried out before construction, strict quality control and safety management should be implemented during the construction process, advanced construction technology and monitoring methods should be adopted, and emergency plans should be formulated so that a quick and effective response can be made when a disaster occurs.





